What is Generative AI
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can generate new content. This includes everything from code snippets to fully rendered images, and even synthetic media like videos and music. Chat GPT and Gemini AI are Large Language Models which widely known applications of Generative AI today.
Generative AI Tools for Software Development
Tools like GitHub Copilot is an example of how generative AI systems help in coding. It suggests entire lines or blocks of code as we type. It’s fascinating to see how deeply AI is integrated into the tools that we use daily. Think about search engines, recommendation systems, IDEs, and even some debugging tools, all powered by AI to enhance our efficiency
Generative AI is not just a tool for creating content faster. It shows a paradigm shift in how we can approach problems and solutions in software development. It offers a way to automate and enhance creativity, reducing the time from concept to product. Whether we are building enterprise applications or games, understanding generative AI will give us a significant edge. Let us see some of the features with examples on how Gen AI can help in software development
Pair coding with LLM(ChatGPT)
Lets ask ChatGPT to write a simple Python function that adds two numbers. Here’s how we can phrase the prompt to ensure clarity and specificity.
Can you write a python function to add two numbers named a and b and return the result? Below is the result from ChatGPT

We can ask ChatGPT to generate a function in Java Script or C# to do the same job. it shall generate code in those languages as well. but when we ask to generate code in C#, we should ask to generate a method. In C#, method is the correct term.
Understanding the domain knowledge of the language, the APIs, and the supporting libraries makes us better developers. It will also make us a better prompter. Knowing the domain knowledge of the business problem is crucial. It will help us find better ways of expressing the solution. We can express it in either prompts or code. So our skills and knowledge are extremely valuable even in the age of prompt generated coding.
Domain Specific Prompting :
By making our prompts more specific and detailed, specifying parameters and conditions helps the model to refine its output.
Let’s ask for a python function that uses NumPy to add two arrays. below is the result from ChatGPT
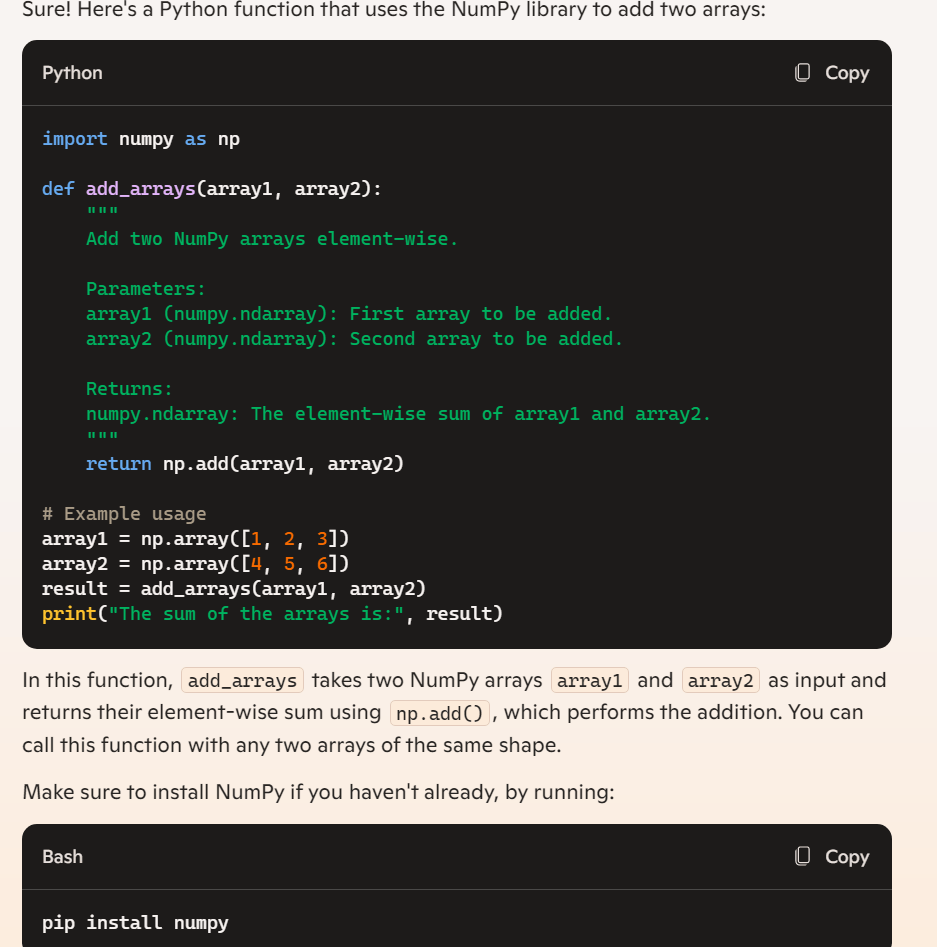
We specified numpy by mentioning it. Chat GPT knows to include the appropriate import. It also knows to use the library’s functions. For example, here it’s using the np.add function to add the two arrays. First, it provides an example of how this function could be used. Then, it offers a quick explanation of the generated code.
Interactive coding with LLM
And now let’s consider the concept of interactive coding to continuously update our code. It doesn’t have to be a one shot situation. We can take the code from GPT and then modify it. We can continue to prompt the model to create better code
To improve a function iteratively by asking the model to write a basic JavaScript function. This function checks if a number is prime.
Below is the result:
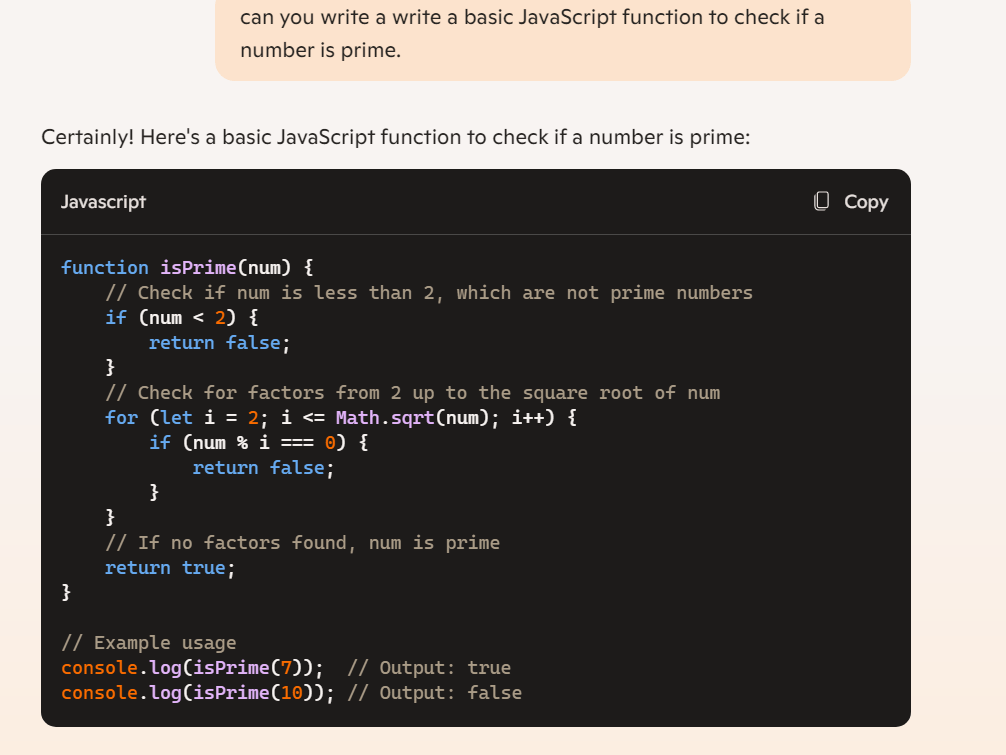

The model responded with some code. It looks like first the function checks if the number is less than 2. Next, it checks a potential factor starting at two. It goes all the way up to the square root of the number. If it ever finds a factor it will return false, but otherwise it will return true. Now, while this isn’t the most efficient algorithm, it’ll definitely work. For now, though, we want to tackle a different problem, which is the lack of error handling. So lets ask the model to add some to make sure that the input is a positive integer.
Below is the result:
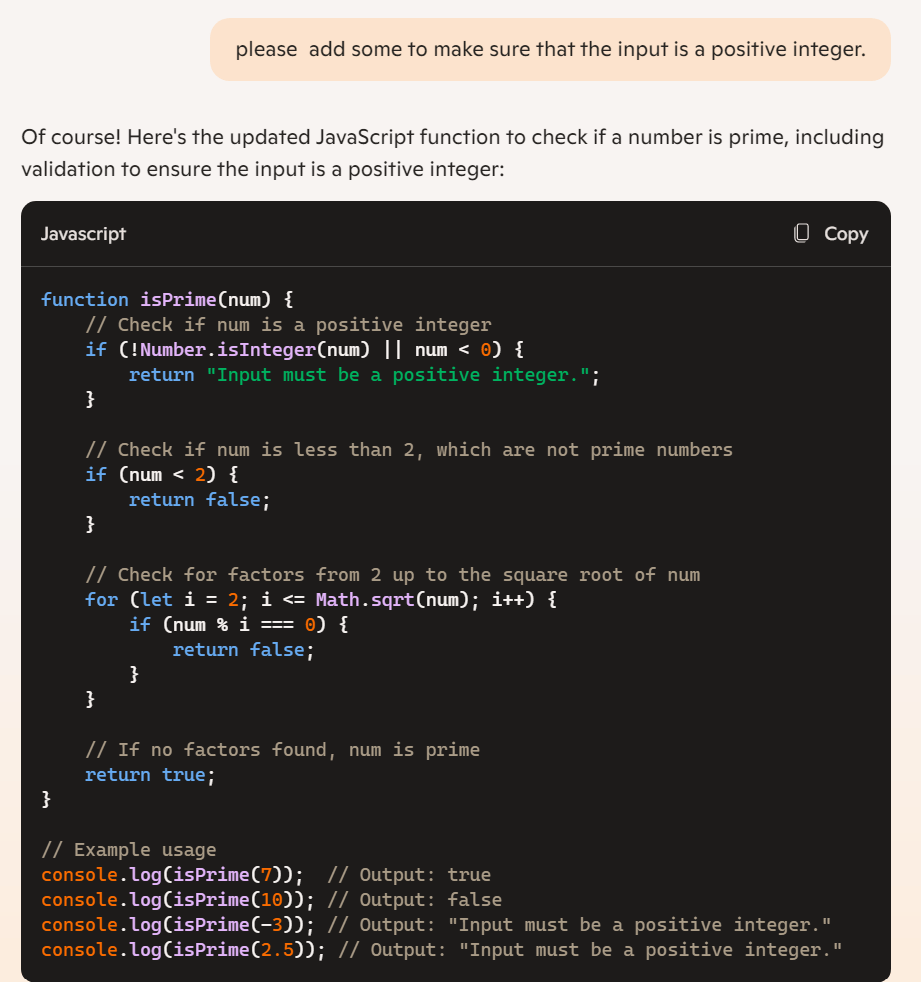

so the model has updated its code to add that error handling in.
First it checks if the input is an integer, and then it checks that the input is positive. If either check fails, the new function will throw an error. Notice that the rest of the function is identical to what we had before.
Below that, the example usage code has been updated to use try and catch. This change is to test the error handling that was just added.
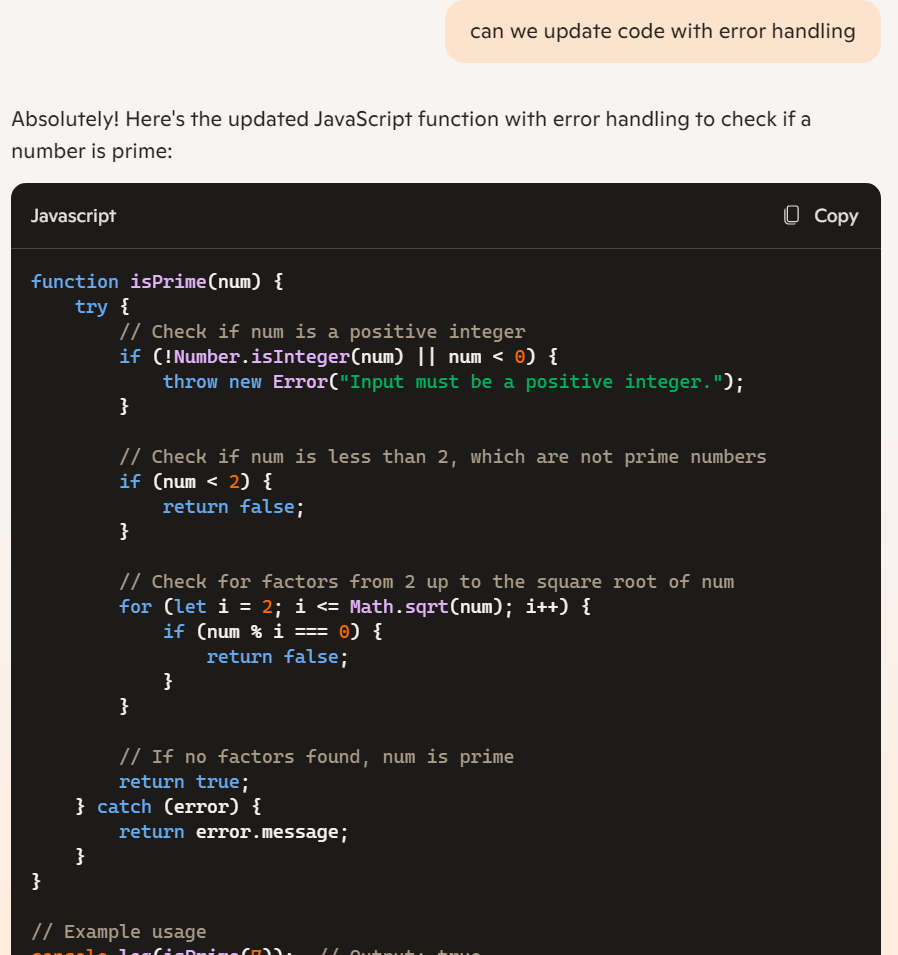
This is pretty useful as well.
Conclusion
In general, vague prompts can lead to ambiguous outputs. Just like a human colleague, the model requests more details. It does this if we don’t specify proper details of what it has to do.
So when using prompts for code, or for anything really, but maybe especially for code, we should be specific. We have to use clear language. We must give as much context as necessary for the model to successfully finish the task.
So these are the basic usages of Generative AI models in Software Development
To be continued…


